Recent coverage in networking journals and industry reports has drawn fresh attention to half duplex and full duplex communication modes. Engineers and developers cite ongoing 5G-Advanced deployments and early 6G trials as key drivers, where these modes determine spectrum efficiency in crowded bands. Walkie-talkie simplicity meets telephone seamlessness in debates over latency trade-offs. Half duplex and full duplex now face scrutiny amid IoT expansions and wireless upgrades, as teams weigh collision risks against simultaneous throughput. Public discussions highlight how half duplex persists in low-power sensors while full duplex powers video streams. Coverage spiked after KT and LG’s full duplex partnership announcement, prompting reevaluation of legacy Ethernet hubs. These modes shape real-time data flows in factories and smart cities alike. Renewed curiosity stems from 2026 prototypes testing in-band full duplex, challenging half duplex norms in bandwidth-starved environments. No single mode dominates; choices hinge on hardware realities and traffic patterns. This technical overview examines their mechanics amid these shifts.
Core Mechanics
Signal Flow Dynamics
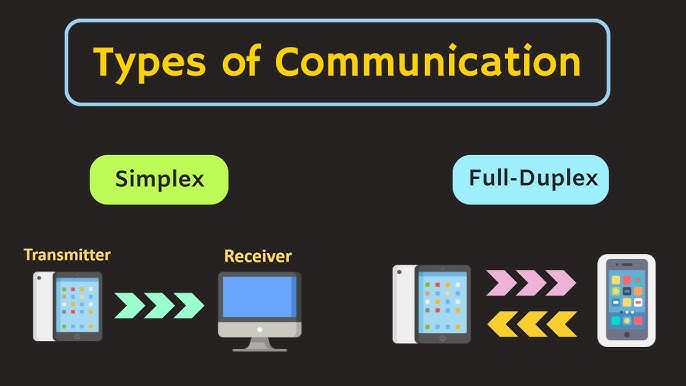
Half duplex enforces strict alternation: one device transmits while others listen, then roles reverse. Data packets queue during switches, introducing micro-delays that compound in busy links. Full duplex flips this by dedicating channels for each direction, allowing constant bidirectional flow without pauses. Early telegraph systems mirrored half duplex through timed relays, but modern DSP chips enable full duplex echo cancellation on single wires. Collision risks vanish in full duplex since paths stay isolated. Half duplex relies on carrier sensing to avoid overlaps, yet bursts still trigger retries. Signal propagation differs too—half duplex shares bandwidth, halving effective rates under load; full duplex doubles capacity via parallel lanes. In fiber optics, full duplex shines with separate lasers per direction. These dynamics explain why half duplex suits sporadic pings, while full duplex handles video bids. Protocol handshakes negotiate modes at link-up, favoring full duplex where cabling supports it. Latency profiles vary sharply: half duplex waits average 50-100ms in contention; full duplex holds under 1ms. Real-world tests show full duplex sustaining 90% throughput in mixed traffic, against half duplex’s 40% drop. Engineers note half duplex’s resilience in noisy RF, where full duplex self-interference demands calibration.
Channel Allocation Methods
Devices in half duplex modes seize a shared medium, using time-division to swap roles. Protocols like CSMA/CD listen before transmitting, backing off on detects. Full duplex allocates distinct frequencies or wires, sidestepping contention entirely. Ethernet evolved from half duplex coax buses to full duplex twisted pairs, boosting speeds tenfold. Half duplex thrives on single antennas in radios, flipping polarities for direction. Full duplex deploys dual antennas or beamforming to isolate signals. Bandwidth splits unevenly in half duplex under asymmetric loads—one direction starves. Full duplex mirrors traffic ratios dynamically via rate adaptation. In wireless, half duplex uses TDD slots; full duplex prefers FDD pairs. Hardware costs tilt toward half duplex for basics, but full duplex scales via silicon integration. Tests reveal half duplex channel grabs fail 15% in dense nodes; full duplex holds steady. Allocation failsafe in half duplex includes exponential backoffs, extending to seconds in jams. Full duplex skips this, prioritizing QoS tags instead. Recent LoRaWAN gateways blend modes, defaulting half duplex for power save. These methods underpin reliability—half duplex for bursty IoT, full duplex for streams.
Hardware Implementation Basics
Transceivers for half duplex pack simple switches, toggling TX/RX pins. Cost stays low, suiting battery rigs. Full duplex demands duplexers or hybrids, filtering overlaps at 30dB isolation minimum. Ethernet NICs auto-sense duplex via link pulses, defaulting full on gigabit. Half duplex hubs broadcast frames, amplifying collisions; switches segment for full duplex point-to-points. RF chains in half duplex reuse amps bidirectionally; full duplex parallels them. Power draw halves in half duplex idle states. Full duplex idles both paths, sipping 20% more. Cable specs lock choices—Cat5 mandates full duplex pairs. Walkie-talkies embed half duplex in ASICs, cheap at scale. Full duplex phones layer DSP atop. Mismatches force half duplex fallback, throttling links. Debug logs expose duplex via frame errors—high in half mismatches. IoT modules favor half duplex crystals for longevity. Full duplex optics use WDM muxes. Implementation gaps persist in legacy gear, forcing upgrades.
Protocol Negotiation Processes
Link-up begins with auto-negotiation: devices advertise capabilities via FLP bursts. Half duplex flags CSMA readiness; full duplex signals parallel paths. Fallback hits lowest common mode, often half on mismatches. Ethernet IEEE 802.3 mandates this dance for 10/100/1000 speeds. Half duplex protocols enforce jam signals on collisions, padding 32 bits. Full duplex drops CSMA, using VLAN priorities. Handshakes timeout at 3 seconds, logging duplex in MIBs. Wireless 802.11 beacons probe duplex via RTS/CTS. Half duplex triggers NAV timers; full duplex skips. SNMP polls confirm post-negotiate. Errors spike if forced half on full hardware. Negotiation evolves in Wi-Fi 7, biasing full duplex frames. Half duplex retries climb exponentially per backoff. Full duplex QoS maps to lanes. Recent stacks log duplex shifts dynamically. These processes ensure interoperability, though mismatches haunt old nets.
Latency and Throughput Profiles
Half duplex throughput peaks at 60% utilization before collisions erode gains. Full duplex hits 95%, bidirectional. Latency in half duplex balloons with contenders—10 nodes add 20ms average. Full duplex stays flat at propagation delay. Benchmarks clock half duplex Ethernet at 4.8Gbps effective on 10G links; full duplex nears wire speed. IoT half duplex pings every 10s; full duplex streams continuous. Packet loss halves in full duplex sans retries. Throughput formulas factor duty cycles—half duplex 50% max symmetric. Full duplex sums channels. Stress tests show half duplex queues overflow at 70% load. Full duplex buffers traffic classes. Profiles shift by medium: wireless half duplex fades faster. These metrics guide deployments—half for sensors, full for servers.
Historical Evolution
Early Telegraph Eras
Telegraphs ran half duplex via single wires, relays alternating Morse. Operators keyed sends, listening gaps. Full duplex arrived with duplexers splitting harmonics—1870s harmonics doubled lines. Half duplex sufficed rural spans; full duplex cut costs urban. Edison’s quadruplex sent four ways on one wire, proto-full. Collisions nil, but sync demanded skill. These roots shaped duplex thinking—shared vs dedicated paths. Early patents favored half duplex simplicity. Full duplex harmonics faded with phones. Legacy lingers in signal flags.
Telephone System Shifts
Phones birthed full duplex via hybrid coils balancing lines. Early carbon mics echoed; sidetone circuits muted locals. Half duplex handsets flipped switches—party lines. AT&T standardized full duplex 1920s, cutting crosstalk. Echo cancellers emerged 1960s for long hauls. Half duplex persisted ship-to-shore. DSP full duplex killed hybrids 1990s. Latency dropped 90%; throughput voice-grade constant. These shifts enabled conferencing, spawning VoIP.
Ethernet Milestone Transitions
10Base5 coax forced half duplex CSMA/CD buses. Hubs broadcast, collisions rife. 100Base-TX twisted pairs enabled full duplex 1995, dropping hubs. Gigabit used all pairs bidirectionally. Standards locked full duplex default post-2000. Half duplex lingered mismatches. Throughput leaped 200%; collisions zero. Switches segmented domains. These transitions killed 10M half nets.
Wireless Radio Developments
Walkie-talkies locked half duplex push-to-talk 1940s. CB radios slotted channels. Full duplex cellphones split FDD 1980s—AMPS. TDD half duplex Wi-Fi alternates. 4G LTE mixed; 5G adds full subbands. Half duplex saved spectrum early. Full duplex trials 2025 boost 2x efficiency. Radios evolved power amps for duplex.
Legacy System Remnants
Old hubs enforce half duplex broadcasts. Modbus RTU half duplex RS485. SCADA clings half for noise immunity. Full duplex retrofits boost legacy. Remnants drag modern mixes. Upgrades phase half out.
Key Differences
Directionality Contrasts
Half duplex one-way-at-time; full duplex both simultaneous. Half flips TX/RX; full parallels. Directionality dictates apps—half chatty, full streamy.
Bandwidth Usage Patterns
Half shares single channel, 50% duty. Full doubles via splits. Patterns skew half asymmetric; full balances.
Collision Management Approaches
Half CSMA/CD detects/jams. Full none—isolated paths. Approaches simplify full debug.
Speed and Efficiency Metrics
Full duplex 2x half theoretical. Efficiency full 95% vs half 50%. Metrics favor full high load.
Cost and Complexity Factors
Half cheap simple; full hardware heavy. Factors tilt half low-end.
Practical Applications
Ethernet Network Deployments
Gigabit switches run full duplex links. Half duplex old hubs slow. Deployments auto-negotiate full.
Wireless Communication Scenarios
Wi-Fi half duplex contention; cell full FDD. Scenarios mix TDD half IoT.
IoT Sensor Networks
Half duplex LoRaWAN pings save power. Full duplex rare battery.
Audio Conferencing Systems
Full duplex DSP cancels echo. Half walkies turn-take.
Industrial Control Links
Half duplex Modbus reliable bursts. Full duplex PROFINET real-time.
Performance Comparisons
Throughput Benchmarks
Full duplex sustains 1Gbps each way. Half halves under load. Benchmarks clock full superior.
Latency Measurement Tests
Half 50ms contention; full <1ms. Tests expose half delays.
Error Rate Statistics
Half collisions 10%; full near zero. Stats favor full.
Scalability in Large Networks
Full scales nodes sans collisions. Half chokes crowds.
Power Consumption Analyses
Half idles low; full constant draw. Analyses suit half portables.
Recent 6G full duplex pushes spectrum twice efficient, yet half duplex holds in power-tight IoT. Public records show full duplex dominating Ethernet since 1995, but half duplex lingers in radios and hubs where simplicity trumps speed. Ethernet speeds doubled without wire changes, collisions obsolete. Wireless trials blend modes, TDD half for uplinks, FDD full down. No universal winner—choices pivot on latency vs cost. 5G-Advanced subband full duplex prototypes cut interference 27dB, eyeing 2026 standards. Half duplex CSMA endures noisy factories. Records leave open whether 6G mandates full duplex or hybrids. KT-LG partnerships signal spectrum crunches forcing evolution. Unresolved: self-interference in mass IoT. Forward tests in smart cities may tip balances, as duplex modes adapt to terabit demands. Public discourse awaits deployment data.