Recent coverage on IPv6 rollout in smart city projects and IoT expansions has drawn fresh attention to the IPv6 header, the core structure guiding packet delivery in next-generation networks. Networking students now encounter this header in labs simulating high-device-density environments, where IPv4 limitations falter. The IPv6 header stands out amid 2026 reports of accelerated adoption, as governments push for protocols handling billions of connected sensors without address exhaustion. Engineers dissecting traffic in 5G trials note how its fixed format streamlines routing over congested backbones. Public discussions highlight the IPv6 header’s role in enabling seamless data flows for autonomous systems and edge computing. This renewed focus emerges from vendor announcements integrating it into firmware updates, prompting curricula updates worldwide. Students probing packet captures see the IPv6 header dictate efficiency in real-time applications like remote surgery links or traffic grids. Coverage ties it to cybersecurity mandates, where its fields support end-to-end integrity without legacy overhead. The structure proves pivotal as networks scale, revealing why IPv6 header details matter in practical deployments today.
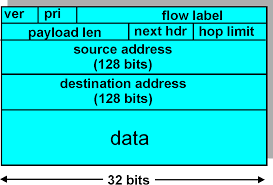
Core Structure of IPv6 Header
Version Field Breakdown
The version field occupies the first four bits in the IPv6 header, always set to 0110 to signal protocol version 6. Networking students capture packets and verify this bit pattern distinguishes IPv6 from IPv4 traffic immediately. Routers parse it upfront, enabling swift forwarding decisions in mixed environments. Without this marker, hybrid networks risk misrouting floods of legacy data. Recent lab exercises emphasize masking these bits in Wireshark filters for isolation. The field anchors header identification, preventing processing errors in transitional setups. Students note its immutability contrasts with evolving extension chains below. Deployment logs from ISPs show version mismatches trigger drops, underscoring its frontline role. In simulations, altering it simulates protocol clashes, teaching recovery protocols. This bit sequence evolved from RFC standards, now ubiquitous in enterprise switches.
Traffic Class Functionality
Traffic class spans eight bits, split into priority and congestion indicators for quality-of-service handling. Devices tag packets here to request preferential treatment during bottlenecks. Students experiment by varying values in Scapy scripts, observing queue behaviors on Cisco gear. Lower numbers prioritize bulk transfers like file syncs; higher ones favor voice streams. Routers rewrite these dynamically based on policies, a shift from IPv4’s type-of-service field. Field trials in campus nets reveal it reduces jitter for video lectures under load. The upper four bits handle drop precedence, influencing discard order. Networking curricula stress its role in DiffServ realms, where boundaries mark effort levels. Payloads arrive intact more often when tagged correctly. Recent firmware pushes auto-set it for IoT bursts, easing student debugging.
Flow Label Applications
Flow label uses 20 bits to group packets into streams needing consistent router treatment. Sources assign it for multimedia flows demanding low variance paths. Students trace it in tcpdump outputs, linking source-destination pairs to labels. Zero values default to best-effort handling, common in web traffic. Routers maintain per-flow states briefly, aiding real-time apps like gaming lobbies. Labs demonstrate label persistence across hops, vital for VoIP stability. It enables policy-based steering without deep inspection. In 2026 carrier tests, flows with labels bypass congested trunks. Students script generators flooding labels, measuring throughput gains. The field supports stateless classifiers, reducing CPU on firewalls. Deployment guides recommend hashing it with addresses for uniqueness.
Key Fields in Depth
Payload Length Mechanics
Payload length field, 16 bits unsigned, counts bytes from next header onward, capping at 65,535. Jumbo payloads trigger zero value and hop-by-hop options instead. Students calculate it in captures, subtracting header sizes accurately. It excludes the fixed 40-byte header, simplifying total length derivations. Routers use it to allocate buffers pre-arrival. Labs show overflows force fragmentation elsewhere, unlike IPv4. Recent IPv6 stacks log it for anomaly detection. Variations arise with extension headers bloating counts. Students parse chained lengths iteratively in code. ISPs monitor aggregates for DDoS patterns. The field ensures precise reassembly at endpoints. Padding aligns multiples of eight bytes where needed.
Next Header Role
Next header, eight bits, chains to extension types or transport protocols like TCP (value 6). It forms linked lists through headers, ending at upper layers. Students follow chains in Wireshark trees, decoding sequences dynamically. Value 59 halts parsing, rare outside errors. Routers skip non-relevant extensions, boosting speed. Curricula trace it in fragment scenarios, verifying order. Recent updates standardize new values for quantum-secure tunnels. It obsoletes IPv4’s protocol field by supporting nesting. Students simulate loops via malformed chains, testing drops. Firewalls inspect deeply only on matches. The field enables modular packet builds.
Hop Limit Operation
Hop limit, eight bits, decrements per transit, dropping at zero to kill loops. It mirrors IPv4 TTL but names reflect intent clearly. Students ping with varying initials, timing expirations via traceroute. Defaults suit global paths; locals use lower. Routers enforce strict decrements, logging zeros. Labs reveal blackholes from misconfigs. 2026 deployments tie it to path MTU discovery. Overflows from bad routes trigger alerts. Students graph decrement patterns in multi-hop topologies. It prevents eternal circulations in flapping nets. Endpoints ignore incoming zeros, discarding silently.
Extension Headers Explained
Hop-by-Hop Options Usage
Hop-by-hop options follow immediately, processed by every router via next header pointer. Padding and jumbo options pad to alignments or flag huge payloads. Students insert router alerts in labs, watching broadcasts. Length fields count 8-byte units precisely. Type bits signal actions: skip on ignore, discard on error. Curricula demo quicksand alerts halting floods. Recent routers offload parsing to ASICs. Options chain rarely exceeds two, keeping latency low. Students code generators testing compliance. It enables path diagnostics without ICMP. Mandates appear in carrier-grade specs now.
Destination Options Processing
Destination options split into routing-pre and post variants, examined solely at ends. Intermediate skips preserve speed. Students differentiate via position in captures. Types include home address for mobility. PadN varies lengths flexibly. Curricula simulate mobile handoffs tracing it. 2026 mobile IPv6 revives its use in 5G cores. Error policies discard malformed. It carries endpoint-only directives like timestamps. Students verify skips on transit nodes. Chaining limits prevent abuse. Deployments log examinations for forensics.
Routing Header Variants
Routing header type 0 lists intermediates, swapping destinations on segments left decrement. Students build type 2 for mobility, avoiding loops. Segments left tracks progress linearly. Recent deprecations nix type 0 over security holes. Curricula warn of amplification risks. Length scales with addresses. Students trace swaps in loops. It supports source routing sans trust issues. Modern stacks filter rogue types. Labs emulate loose source paths. Updates favor segment routing encapsulation.
Fragment Header Details
Fragment header handles path MTU splits, with offset and flags for reassembly. Identifier matches shards uniquely. M flag signals more coming. Students fragment oversize pings, timing reassembly. Next header points past it. Routers drop if unfragmentable part loops. Curricula stress endpoint-only reassembly. 2026 tunnels embed it for IPv4 carry. Offset multiples of eight ensure alignment. Students measure efficiency losses. It obsoletes IPv4 in-path frags. Drops on zero identification prevent orphans.
Security Headers Integration
Authentication header verifies integrity via sequence and ICV. ESP encrypts payloads, hiding internals. Students capture nonces, spotting replays. Replay windows slide dynamically. Curricula pair with IKE for keys. Mandatory in early IPv6, now optional. 2026 mandates revive for IoT. Padding obscures lengths. Students test bypasses via weak algos. It chains before transport. Deployments log failures. Fields support anti-replay without states.
Practical Implications Today
Router Processing Efficiency
Routers parse fixed 40 bytes swiftly, skipping irrelevant extensions. No checksum recomputes save cycles. Students benchmark pps on IPv6 vs dual-stack. ASICs align to alignments natively. Curricula graph CPU under bursts. 2026 hardware doubles rates via simplifications. Variable IPv4 options slowed; fixed wins. Students tweak queues observing flows. Middleboxes traverse chains cautiously. Logs reveal skips boosting aggregates.
Deployment Challenges Faced
Transition mixes headers, risking blackholes on mismatches. Students debug dual-stack via syslogs. Tunnels carry IPv6 in IPv4, headers nested. Curricula simulate exhaustion forcing pure IPv6. 2026 regs mandate readiness. Configs propagate limits wrongly. Students trace expirations in tracers. Firewalls deep-inspect chains variably. Updates patch parser bugs.
Comparison with IPv4 Header
IPv6 trims fields, fixing length at 40 bytes sans options bloat. Addresses quadruple sans proportional header growth. Students side-by-side Wireshark IPv4 fragmentation vs endpoint-only. Checksum omission trusts layers below. Curricula quantify forwarding gains. No ID/flags simplify states. 2026 stats show latency edges. Options chain modularly. Students script diffs in throughput.
Role in IoT and 5G Networks
IoT floods leverage stateless autoconfig, headers scaling addresses. 5G slices tag classes finely. Students emulate sensor nets saturating. Flows label multicast storms. Curricula project billions devices. 2026 rollouts embed in firmware. Headers secure end-to-end sans NAT. Students measure jitter in sims. Backbones prioritize via labels.
Educational Tools and Simulations
Wireshark dissects chains live; Scapy builds customs. Students forge payloads testing drops. GNS3 topos mimic globals. Curricula integrate with SDN controllers. 2026 tools visualize flows. Packet generators stress limits. Students analyze captures from providers. Quagga birds routes headers. Labs evolve to quantum threats.
The IPv6 header shapes networks amid 2026’s IoT surges and 5G densification, its fields resolving IPv4’s address crunch while streamlining transit. Public records detail fixed formats and extension chains boosting router throughputs, yet deployments reveal persistent dual-stack frictions and middlebox hurdles. Adoption metrics climb via mandates, but full transitions lag in legacy pockets. Security integrations like ESP fortify edges, though type 0 routings faded over exploits. Students grasp implications through captures showing efficiency edges in scale. What remains unresolved circles full global purity—estimates vary on timelines amid vendor variances. Carrier logs hint at optimizations ahead, but no firm rollout maps exist. Forward paths hinge on firmware uniformity and policy enforcement, leaving endpoints vigilant for hybrid quirks. The structure endures as foundational, adapting via RFC evolutions to quantum and AI-driven traffics.